1. 재귀 함수
2. DFS 깊이 우선 탐색
2.1. 스텍 프레임
3. BFS 레벨, 너비 우선 탐색
- 재귀 함수
- 재귀 함수는 자기 자신을 호출하는 함수를 말한다.
- 기본적으로 if else를 통해 특정 조건에 자기 자신을 호출하여 원하는 값을 도출해낸다.
- 재귀 함수를 이용한 팩토리얼
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main {
public int DFS(int v) {
if (v == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return v * DFS(v - 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main main = new Main();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int i = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(main.DFS(i));
}
}
1. if else를 사용하여 최종 1에 도달하게 되면 1을 반환하고, 자기 자신을 호출하면서 팩토리얼 로직을 완성하게 된다.
- DFS 깊이 우선 탐색
- DFS는 그래프와 트리 구조에서 사용되는 탐색 알고리즘 중 하나이다.
- 특정 노드에서 시작하여 다음 분기로 넘어가기 전에 해당 분기를 완전히 탐색하는 방법이다.
- 스택 또는 재귀를 사용하여 구현할 수 있다.
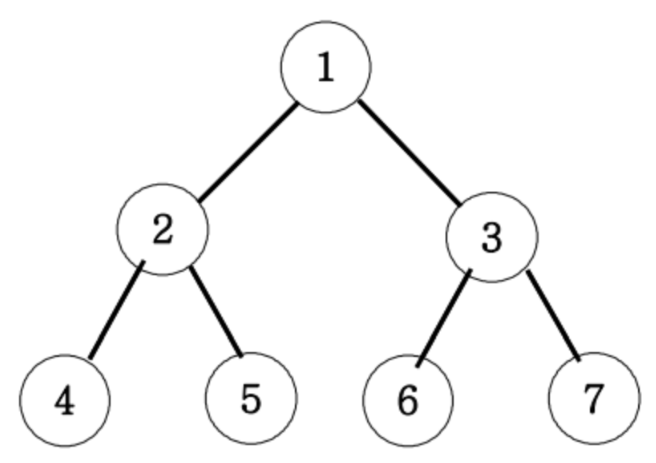
- 전위 순회, 중위 순회, 후위 순회 (부모를 탐색하는 순서를 생각하면 된다.)
1. 전위 순회 : 부모 - 왼쪽 - 오른쪽 (1 2 4 5 3 6 7)
2. 중위 순회 : 왼쪽 - 부모 - 오른쪽 (4 2 5 1 6 3 7)
3. 후위 순회 : 왼쪽 - 오른쪽 - 부모 (4 5 2 6 7 3 1)
- DFS 기본 구조
class Node {
int data;
Node lt, rt;
public Node(int val) {
data = val;
lt = rt = null;
}
}
public class Main {
Node root;
public void DFS(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
} else {
//전위 순회
// System.out.print(root.data+" ");
DFS(root.lt);
//중위 순회
// System.out.print(root.data+" ");
DFS(root.rt);
//후위 순회
// System.out.print(root.data+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main tree = new Main();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.lt = new Node(2);
tree.root.rt = new Node(3);
tree.root.lt.lt = new Node(4);
tree.root.lt.rt = new Node(5);
tree.root.rt.lt = new Node(6);
tree.root.rt.rt = new Node(7);
tree.DFS(tree.root);
}1. DFS는 자식 노드가 둘 다 존재해야 한다.
2. 좌측, 우측 노드를 호출하게 되는데 해당 노드의 값을 추출하는 위치에 따라 전위, 중위, 후위 순회가 결정된다.
- 스택 프레임
- 깊이 우선 탐색에는 스택 프레임이 사용된다.
- 스택 프레임에는 매개변수, 지역변수, 복귀주소 값이 저장된다.
- DFS의 함수들은 Stack에 데이터가 쌓이면서 순서대로 구현되기 때문에, 가장 깊은 곳 (=스택의 제일 윗부분) 의 함수부터 호출되게 된다.
* 스택에 대해서는 별도로 다뤄 볼 것이다.
- BFS 레벨, 너비 우선 탐색
- 그래프와 트리 구조에서 사용되는 탐색 알고리즘 중 하나로, 시작 노드부터 가까운 노드부터 차례대로 탐색하는 방법이다.
- 이 알고리즘은 Queue 자료구조를 사용하여 구현한다.
- BFS는 최단 경로를 찾는데 주로 사용된다.

- BFS 기본 구조
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Node {
int data;
Node lt, rt;
public Node(int val) {
data = val;
lt = rt = null;
}
}
public class Main {
Node root;
public void BFS(Node root) {
Queue<Node> Q = new LinkedList<>();
Q.offer(root);
int L=0;
while (!Q.isEmpty()) {
int len = Q.size();
System.out.print(L + " : ");
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Node cur = Q.poll();
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
if (cur.lt != null) {
Q.offer(cur.lt);
}
if (cur.rt != null) {
Q.offer(cur.rt);
}
}
L++;
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main tree = new Main();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.lt = new Node(2);
tree.root.rt = new Node(3);
tree.root.lt.lt = new Node(4);
tree.root.lt.rt = new Node(5);
tree.root.rt.lt = new Node(6);
tree.root.rt.rt = new Node(7);
tree.BFS(tree.root);
}
}1. Queue를 생성하여, 0 레벨부터 하나씩 내려가면 해당 레벨에 있는 모든 노드를 Queue에 넣고, 하나씩 비교해가면 다음 자식노드가 존재하는지 존재하는 확인하다.
'Programming > CodingTest' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CodingTest - 정렬 (Comparable, compareTo, Collections.sort) (0) | 2023.12.12 |
|---|---|
| CodingTest - Sorting and Searching(정렬, 이분 검색과 결정 알고리즘) (0) | 2023.11.08 |
| CodingTest - HashMap, TreeSet (해쉬, 정렬지원 Set) (0) | 2023.11.01 |
| CodingTest - Two Pointers, Sliding Window (0) | 2023.10.19 |
| CodingTest - 퀵 정렬 (1) | 2023.10.17 |